Write and paraphrase
 Processing Request
Processing Request
The process of writing a work consists of interweaving personal ideas on a subject and appropriating those of specialists, journalists or other authors to paraphrase them. This reformulation must be done well to avoid plagiarism.
![]() Goals
Goals
- Identify resources for writing.
- Use writing strategies.
- Follow modified citation presentation standards.
![]()
Before writing, it is recommended to develop a detailed plan to order and structure your ideas in a logical and coherent way.
- To write your work, consult the presentation page model (.dotx).
![]()
- Develop one idea per paragraph.
- Make short sentences (subject, verb, complement).
- Avoid impersonal sentences such as: it is necessary, it is important to
- Omit repetitions of words.
- Favor the active form sentence rather than the passive form: The cat eats the mouse. The mouse is eaten by the cat.
- Allow time to step back before revising the text.
- Have an acquaintance reread the text.
For more information on how to write a work, do not hesitate to listen to the capsules offered by the Learning Support of the Office of Inclusion and Student Success (BIRÉ) and to consult these Useful resources for writing .
![]()
Paraphrasing is “changing the wording of a message without changing its meaning”. ( Termium )
To paraphrase, it is therefore important to understand the original text well and to use rewriting tips.
![]()
- Replace the most important words (nouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, etc.)
- Maintain the meaning of the author's words.
- Choose synonyms. Check the meaning using a dictionary .
- Change sentence structure.
- Rewrite the sentences by changing the order of the words. Modify relationship markers – coordinating or subordinating –.
- Change parts of speech.
- Replace a noun with a verb, an adjective with a noun, a verb with a noun, etc. The order of the words in the sentence will be changed.
- Make any other changes deemed relevant.
- Compare the paraphrase to the original extract.
- Ensure that the structure and/or the same words have not been used and that the paraphrase contains the ideas of the original text.
![]()
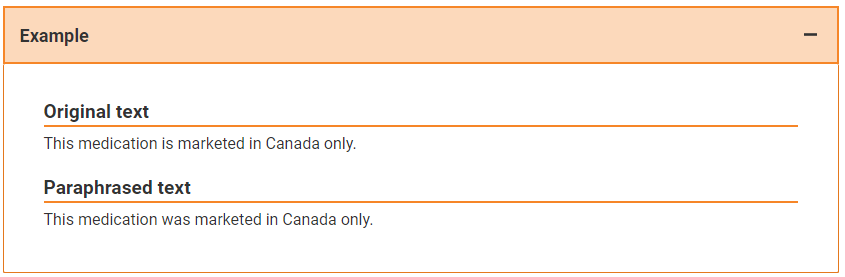
Regardless of the method used, always indicate the reference of the paraphrased text.
![]()
To ensure writing consistency and keep the text understandable, minor edits may need to be made to the citation. For example, words must be added or deleted or pronouns need to be clarified.
Mark any modification of a quotation with square brackets [ ].
![]()
Make this addition to:
- Give explanations about a term.
- Provide additional information.
- Indicate that certain words in the quote have been highlighted.
![]()
Make changes to pronouns, determiners and/or verb endings.
Don't overuse it.
![]()
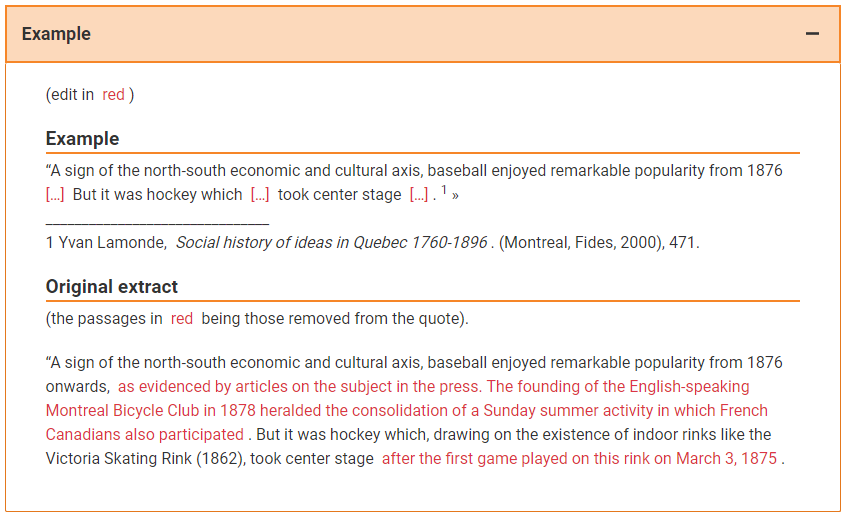
Ignore any part of the text that is not essential to the citation.
Use the ellipsis in square brackets […] to replace the deleted part of the quotation.
![]()
- The use of these writing strategies facilitates the development of a text, in an effective manner, while ensuring compliance with the rules of academic integrity.
 Links/documents
Links/documents
- To go further, register for the Work Writing workshop offered by the SVE (Student Life Services).
- Presentation page template (.dotx) for an academic work.



Generally speaking, the introduction to a work will consist of 3 parts. The first part, the subject brought , will consist of introducing your subject without naming it. For example, the subject can be brought up using a statistic, a historical link or even a current event. The second part, the posed subject , will aim to explicitly name its subject and the way in which it will be approached by indicating the type of work requested (summary, criticism, essay, etc.) The third part, the divided subject , will allow us to name the main ideas of development without explaining them. In short, the introduction can be seen as a funnel in which the subject will be approached from the most global to the most specific.
The development will differ depending on the type of work requested (summary, critique, essay, etc.) Generally speaking, the first sentence of the paragraph will be used to name the main idea addressed and the subsequent sentences will explain this main idea, to argue, make theoretical connections, illustrate using examples, give your opinion or other depending on the type of work requested (summary, critique, essay, etc.). It is therefore important to refer to the requirements of the work to clearly target the nature of the development (argumentative, informative, opinion text, etc.)
The conclusion will have 2 parts. The first part will serve to summarize in a few sentences the main ideas of the text. The second part will be an opening towards an idea which has not been developed and which is linked to the subject of the text. For example, it could be a link to the job market, internships, personal experience, a notable quote, etc. Finally, the conclusion can be thought of as an inverted funnel in which the topic will be restated specifically and then globally.
There are many resources available to help with writing. This section offers a selection of the most relevant resources.
![]() Objective
Objective
- Identify quality documentary resources currently being written.
![]()
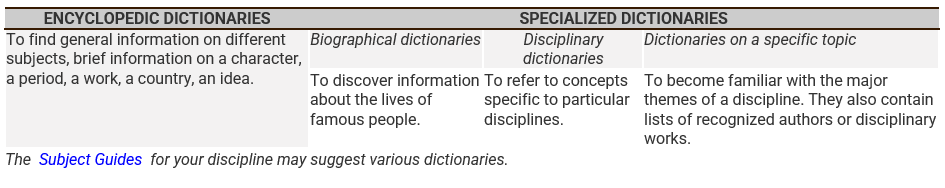
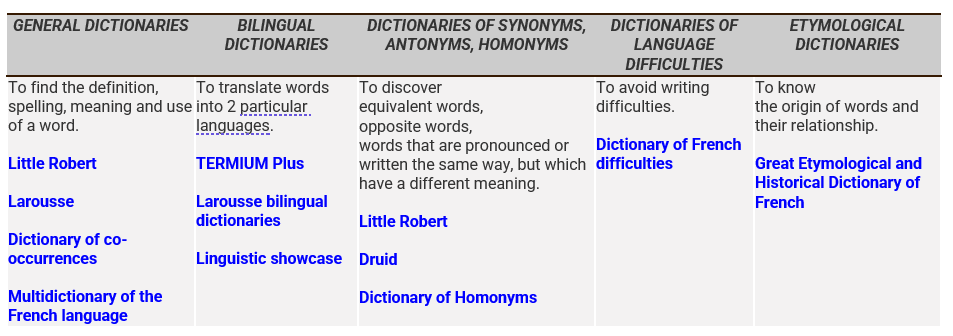
This table indicates for each suggested dictionary the main attraction that characterizes it and suggests resources to consult.
![]()
![]()
Several writing assistance tools are available on the Web but are not all of equal quality. Federal and provincial institutions provide excellent ones that benefit from being better known.
Tools from the Translation Bureau of the Government of Canada:
- The Writer's Guide explains the principles of a language in a clear and simple way as well as the rules for using capital letters, punctuation, writing numbers and more.
- ConjugArt provides the conjugation of nearly 8,000 French verbs
- The Preposition Roll allows you to find the preposition that suits the adjective, verb or adverb
Tool from the Office québécois de la langue française of the Government of Quebec: Linguistic showcase
![]()
Books or web pages to consult for writing advice depending on the type of work to be done.
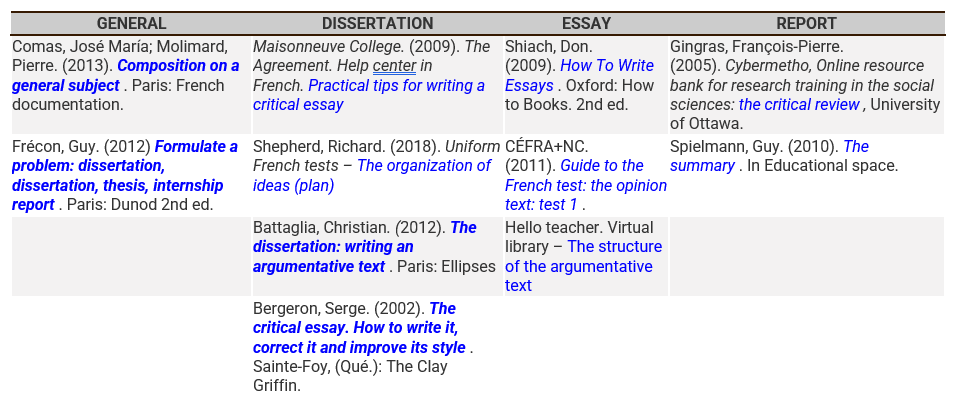
![]()
- Writing skills develop with practice. Keep in mind that even writing professionals consult dictionaries and writing tools.
.png)















